What Is The Definition Of Global Warming In Chemistry
This phenomenon has been observed over the past one or two centuries. An increase in the average temperature of the Earths atmosphere especially a sustained increase great enough to cause changes in the global climate.
 Introduction To Climate Change Climate Change Lesson Global Warming Lesson School Climate
Introduction To Climate Change Climate Change Lesson Global Warming Lesson School Climate
Definition of global warming.

What is the definition of global warming in chemistry. Global warming is the phenomenon of a gradual increase in the temperature near the earths surface. The wavelengths where the molecule absorbs. The Earth has experienced numerous episodes of global warming through its history and currently appears to be undergoing such warming.
Carbon dioxide Of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide CO 2 is the most significant. Different GHGs can have different effects on the Earths warming. They act like a blanket insulating the Earth.
Each year scientists learn more about the consequences of global warming and many agree that environmental economic and health consequences are likely to occur if current trends continue. Heres just a smattering of what we can look forward to. A molecules GWP depends on three factors.
Global warming is the long-term warming of the planets overall temperature. Climate scientists have since the mid-20th century gathered detailed observations of various weather phenomena such as temperatures precipitation and storms and of related influences on climate such as ocean currents and the. Global warming is a phenomenon related to nature.
Natural sources of atmospheric CO 2 include outgassing from volcanoes the combustion and natural decay of organic matter and respiration by aerobic oxygen-using organisms. Global warming is usually used to describe the warming of the climate in the past 200 years which the vast majority of scientists are almost certain has been caused by human activities. Though this warming trend has been going on for a long time its pace has significantly increased in the last hundred years due to the burning of fossil fuels.
Greenhouse gases then radiate heat energy back toward the earth. Global warming is the unusually rapid increase in Earths average surface temperature over the past century primarily due to the greenhouse gases released by people burning fossil fuels. One of the commonly used pieces of evidence that humans are causing global warming is that there is a strong correlation between the increase in global carbon dioxide levels caused by human.
This change has disturbed the climatic pattern of the earth. An increase in the earths atmospheric and oceanic temperatures widely predicted to occur due to an increase in the greenhouse effect resulting especially from pollution A Russian-owned tanker built to traverse the frozen waters of the Arctic completed a journey in record time from Europe to Asia this month auguring the future of. How Does Todays Warming Compare to Past Climate Change.
Melting glaciers early snowmelt and severe droughts will cause more dramatic water. Global warming the phenomenon of increasing average air temperatures near the surface of Earth over the past one to two centuries. Due to the continuous accumulation of greenhouse effect the energy absorbed and emitted by the gas system is not balanced.
Global warming usually refers to human-induced warming of the Earth system whereas climate change can refer to natural as well as anthropogenic change. The two terms are often used interchangeably. Greenhouse gases absorb infrared long-wave heat radiation.
GWP is a measure of how much energy a greenhouse gas would add to atmospheric warming in a given time compared to CO 2. As the human population has increased so has the volume of fossil fuels burned. This heats the earths atmosphere and ultimately contributes to increasingly warmer climates a process known as global warming.
3 However framing global warming as a fundamentally scientific issue allows us to examine the. Earth has experienced climate change in the past without help from humanity. This is the form of the suns energy reflected off the earths surface.
Greenhouse gases GHGs warm the Earth by absorbing energy and slowing the rate at which the energy escapes to space. However the concept of global warming is quite controversial but the scientists have provided relevant data in support of the fact that the temperature. In the context of contributions of different gases to atmospheric warming the concept of global warming potential GWP can be useful.
 Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming Environmental Science Letstute Youtube
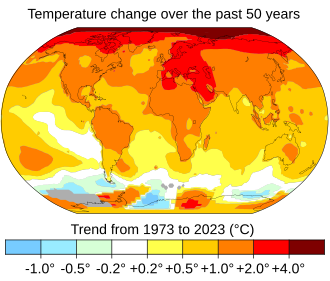 Global Warming Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Global Warming Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
 Global Warming Effects Of Global Warming Global
Global Warming Effects Of Global Warming Global
 Global Warming Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
Global Warming Simple English Wikipedia The Free Encyclopedia
 What Is Global Warming Live Science
What Is Global Warming Live Science
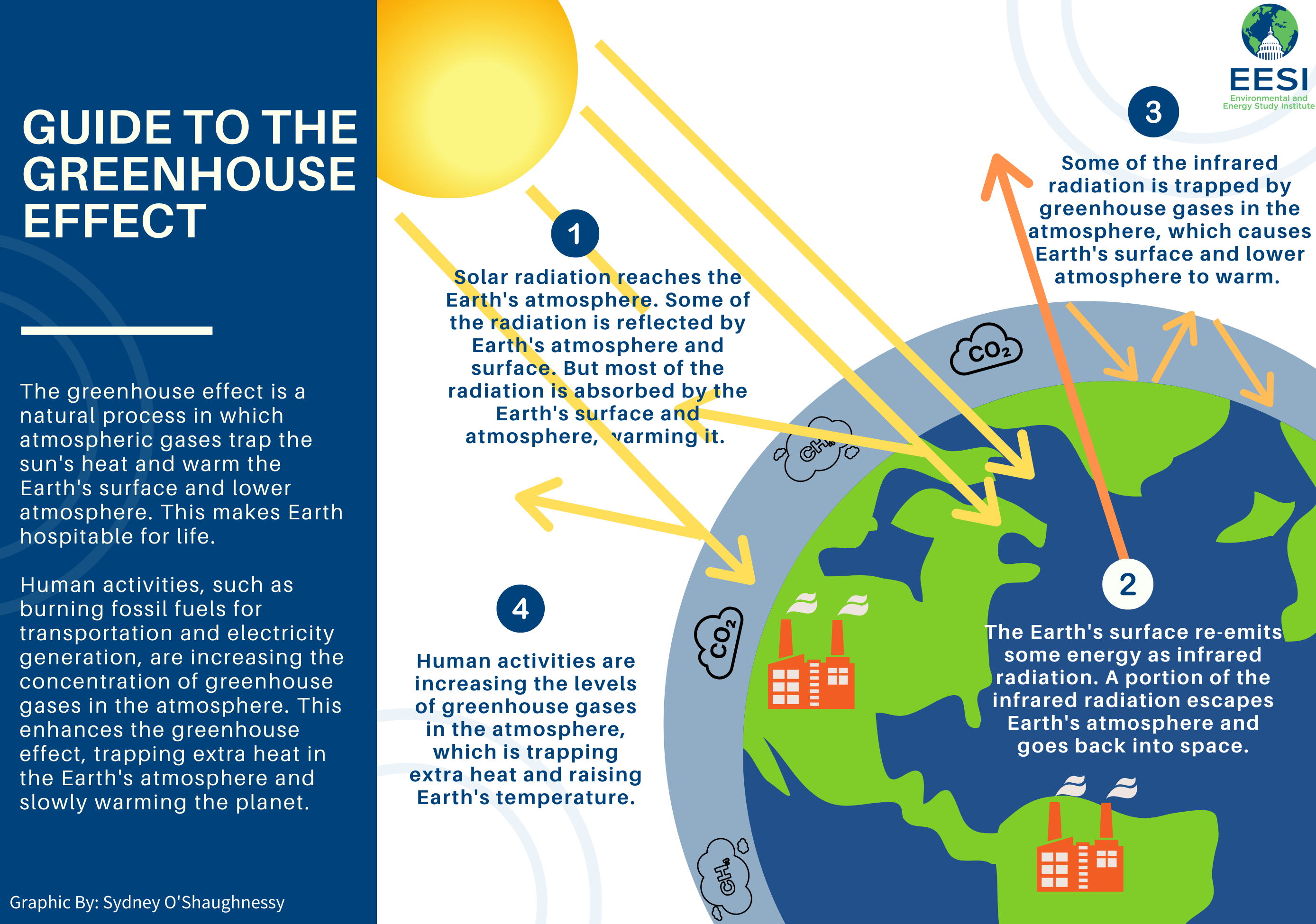 Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
 Global Warming Rising Sea Levels Global Warming Chemistry Global Warming Chemistry Global
Global Warming Rising Sea Levels Global Warming Chemistry Global Warming Chemistry Global
 Image Result For Global Warming Definition Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Global Warming Climate Change
Image Result For Global Warming Definition Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Global Warming Climate Change
 Global Warming Mind Map Global Warming Effects Of Global Warming
Global Warming Mind Map Global Warming Effects Of Global Warming
 Chemistry Biology Evolvingknowledge Ozone Ozonelayer Sicence Climatechange Globalwarming Chemicalreaction Ozone Layer Ozone Global Warming
Chemistry Biology Evolvingknowledge Ozone Ozonelayer Sicence Climatechange Globalwarming Chemicalreaction Ozone Layer Ozone Global Warming
 What Is Global Warming Live Science
What Is Global Warming Live Science
 What Is A Conservatory Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Facts
What Is A Conservatory Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Facts
 5 Effects Of Global Warming That Will Make You Think Infographic Richmondvale Blog
5 Effects Of Global Warming That Will Make You Think Infographic Richmondvale Blog
 Climate Change Abrupt Climate Changes In Earth History Britannica
Climate Change Abrupt Climate Changes In Earth History Britannica
 Causes Of Global Warming Facts And Information
Causes Of Global Warming Facts And Information
 Global Human Green House Gas Emissions By Sector Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Emissions
Global Human Green House Gas Emissions By Sector Greenhouse Gases Ghg Emissions Emissions


Post a Comment for "What Is The Definition Of Global Warming In Chemistry"