Global Burden Of Disease Urbanization
Progress on drinking water and sanitation. Addressing the burden 10 21 Reasons for action.
 The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
Illness and death from diseases caused by contaminated food are a constant threat to public health and a significant impediment to socio-economic development worldwide.
Global burden of disease urbanization. More than half of the global population lived in cities in 2010 a proportion expected to reach 60 in 2030 and 70 in 2050. Although not currently incorporated into the GBD 2015 a recent effort to determine the global burden of leptospirosis estimates approximately 1 million annual cases resulting in almost 3 million disability-adjusted life years. 24 Urbanisation and urban development policy.
Impending global burden of CVD if we do not take action now. Cardiovascular disease CVD is the number one cause of mortality world-wide and places a high medical and socioeconomic burden on developing countries. Moreover the burden of air pollution from all sources considered in the CRA indoor outdoor occu-.
Urban leptospirosis has also been reported in Nairobi. During week two we will dive into global health security. 2015 update and MDG.
The original GBD study was commissioned in 1992 by the World Bank for its 1993 World Development Report on Investing in Health recommended cost-effective intervention packages for countries at different levels of development Underpinning these analyses was the first Global Burden of Disease GBD study carried out by. The high current burdens of noncommunicable diseases NCDs are highlighted by the estimates provided by the Global Burden of Disease Study 11 and in the World Health Report 1999 12 which indicate that these disorders together contributed to 59 of global mortality 317 million deaths and 43 of the global burden of disease in 1998. Developing Asia is estimated to contribute approxi-mately two-thirds of the global burden Table 1.
Food water energy and the threats of a changing climate. GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017.
Several NCDs such as cardiovascular diseases CVD cancers diabetes and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Generating Evidence Guiding Policy Main Findings from the Sub-Saharan Africa Regional Edition World Bank Group. Global Trends in Obesity In 2005 about 16 billion adults age 15 throughout the world were overweight BMI25.
Urbanisation is associated with an increased prevalence of NCD risk behaviours which are increasing at a rapid rate. Food water energy and the threats of a changing climate. Most comprehensive global studyanalysing 286 causes of death 369 diseases and injuries and 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territoriesreveals how well the worlds population were prepared in terms of underlying health for the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
However the study did not report the percentage of cases found in urban versus rural environments. NCD Burden of Disease. Cardiovascular disease and urbanization 6 11 Urban growth in the 21st Century 6 12 The relationship between urbanization and heart health 6 13 Cardiovascular disease burden 6 14 Why a global response is needed 8 Chapter Two.
By 2015 WHO projects that approximately 23 billion adults will be overweight and 700 million obese. A systemic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. The burden of disease due to urban air pollution occurs predominantly in developing countries.
Global regional and national incidence prevalence and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories 19902017. Including 400 million who were obese BMI30. Our understanding of CVD and its evolution over the last 100 years has altered considerably.
Raising heart-healthy children in todays cities reveals the cross-cutting links between. Cdc-pdf PDF 86 pages External Lancet. During week two we will dive into global health security.
To measure the global and regional burden of foodborne disease FBD the World Health Organization WHO established the Foodborne. Global regional and national life expectancy all-cause mortality and cause-specific mortality for the 249 cuases of death 1980-2015. Week three will cover the global burden of disease infectious disease the rise of non-communicable diseases mental health and access to care.
To our knowledge we present the first global and regional estimates of the disease burden of the most important foodborne bacterial protozoal and viral diseases. Global Burden of Disease. Returns for individuals society and the economy 10.
We synthesized data on the number of foodborne illnesses sequelae deaths and Disability Adjusted Life Years DALYs for all diseases with sufficient data. The first global burden of disease study in the 1990s. Week three will cover the global burden of disease infectious disease the rise of non-communicable diseases mental health and access to care.
Dr Kathryn Taubert Chief Science Officer World Heart Federation The report on Urbanization and cardiovascular disease.
 Pdf Non Communicable Diseases And Urbanization In African Cities A Narrative Review
Pdf Non Communicable Diseases And Urbanization In African Cities A Narrative Review
 Global Burden Of Disease 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators 2017 Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of Assessment Analysis Risk Factors
Global Burden Of Disease 2016 Risk Factors Collaborators 2017 Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of Assessment Analysis Risk Factors
 Global And Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates For 2019 And Projections For 2030 And 2045 Results From The International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition Diabetes Research And Clinical Practice
Global And Regional Diabetes Prevalence Estimates For 2019 And Projections For 2030 And 2045 Results From The International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas 9th Edition Diabetes Research And Clinical Practice
 The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
 Global Regional And National Dengue Burden From 1990 To 2017 A Systematic Analysis Based On The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 Eclinicalmedicine
Global Regional And National Dengue Burden From 1990 To 2017 A Systematic Analysis Based On The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 Eclinicalmedicine
 The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
 Burden Of Non Communicable Diseases In Sub Saharan Africa 1990 2017 Results From The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet Global Health
Burden Of Non Communicable Diseases In Sub Saharan Africa 1990 2017 Results From The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet Global Health
 Global Regional And National Incidence Prevalence And Years Lived With Disability For 354 Diseases And Injuries For 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet
Global Regional And National Incidence Prevalence And Years Lived With Disability For 354 Diseases And Injuries For 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet
 Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of 79 Behavioural Environmental And Occupational And Metabolic Risks Or Clusters Of Risks 1990 2015 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2015 The Lancet
Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of 79 Behavioural Environmental And Occupational And Metabolic Risks Or Clusters Of Risks 1990 2015 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2015 The Lancet
 Who Double Burden Of Malnutrition
Who Double Burden Of Malnutrition
 Burden Of Non Communicable Diseases In Sub Saharan Africa 1990 2017 Results From The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet Global Health
Burden Of Non Communicable Diseases In Sub Saharan Africa 1990 2017 Results From The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017 The Lancet Global Health
 Urbanisation And Infectious Diseases In A Globalised World The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Urbanisation And Infectious Diseases In A Globalised World The Lancet Infectious Diseases
 Urban Associated Diseases Candidate Diseases Environmental Risk Factors And A Path Forward Sciencedirect
Urban Associated Diseases Candidate Diseases Environmental Risk Factors And A Path Forward Sciencedirect
 The Global Regional And National Burden Of Colorectal Cancer And Its Attributable Risk Factors In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017
The Global Regional And National Burden Of Colorectal Cancer And Its Attributable Risk Factors In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2017
 Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of 79 Behavioural Environmental And Occupational And Metabolic Risks Or Clusters Of Risks 1990 2015 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2015 The Lancet
Global Regional And National Comparative Risk Assessment Of 79 Behavioural Environmental And Occupational And Metabolic Risks Or Clusters Of Risks 1990 2015 A Systematic Analysis For The Global Burden Of Disease Study 2015 The Lancet
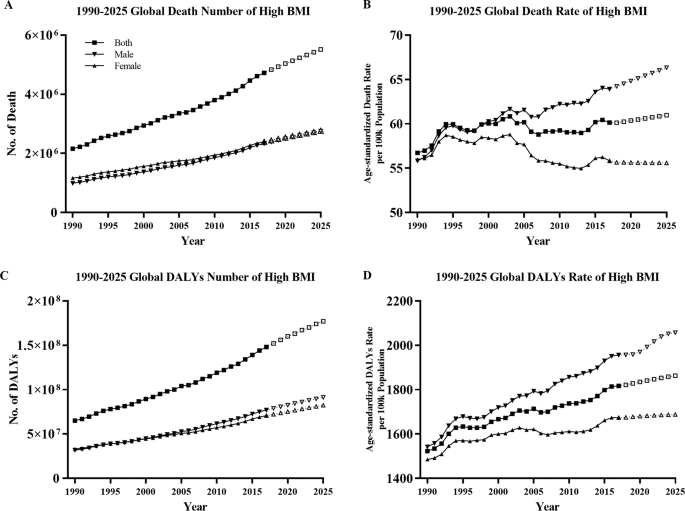
 Global Burden Of Noncommunicable Disease Attributable To High Body Mass Index In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 Springerlink
Global Burden Of Noncommunicable Disease Attributable To High Body Mass Index In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 Springerlink
 The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
 The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
The Global Burden Of Disease World Bank Group
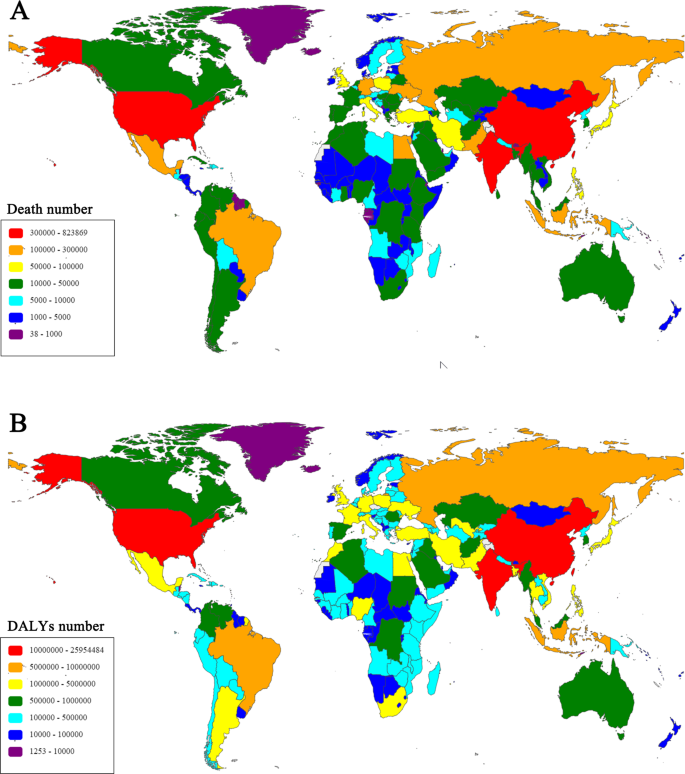 Global Burden Of Noncommunicable Disease Attributable To High Body Mass Index In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 Springerlink
Global Burden Of Noncommunicable Disease Attributable To High Body Mass Index In 195 Countries And Territories 1990 2017 Springerlink
Post a Comment for "Global Burden Of Disease Urbanization"