Global Cooling During The Eocene-oligocene Climate Transition
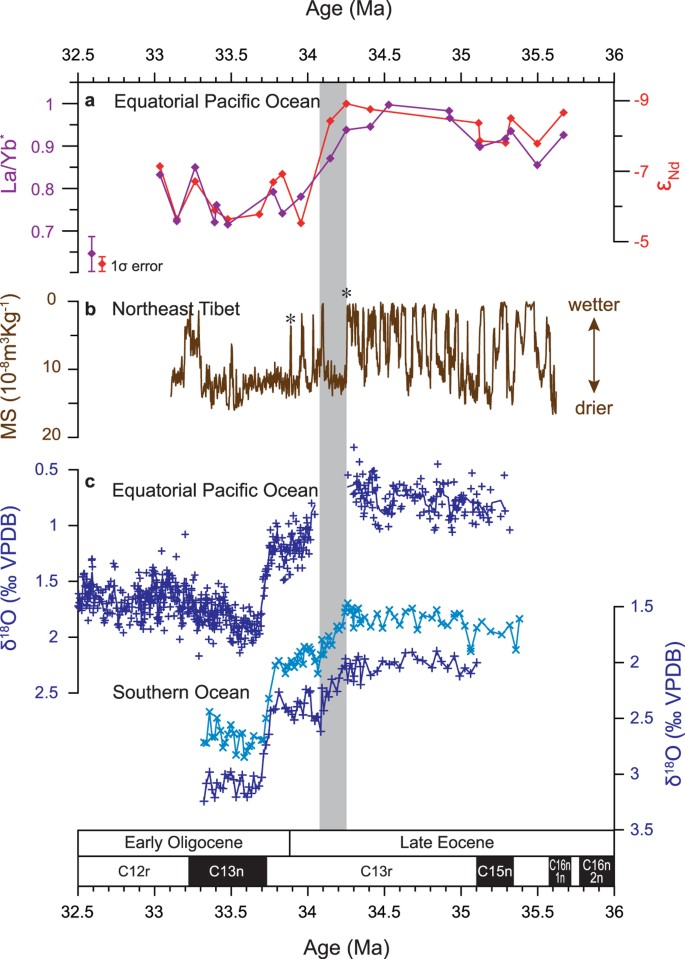
When compared to the GPTS the Early Oligocene to stantiates previous propositions that Pliocene climate deterioration Late Eocene time interval is characterized by two long reversed chrons C12r and or late Miocene global cooling essentially governed Asian deposi-. Diverse geological evidence from around the world indicates cooling ice growth sea-level fall and accelerated extinction at this time.
 The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
The Eocene-Oligocene transition between ca.

Global cooling during the eocene-oligocene climate transition. Falling atmospheric CO2levels led to cooling through the Eocene and the expansion of Antarctic ice sheets close to their modern size near the beginning of the Oligocene a period of poorly documented cli- mate. At sites 511 and 336 for which E-O transition. The Eocene-Oligocene climate transition EOCT is often cited as the most important interval of climate change during the Cenozoic because it heralds the switch from the warmer equable global greenhouse climates of the late Mesozoic and early Paleogene to the cooler more seasonal icehouse climates.
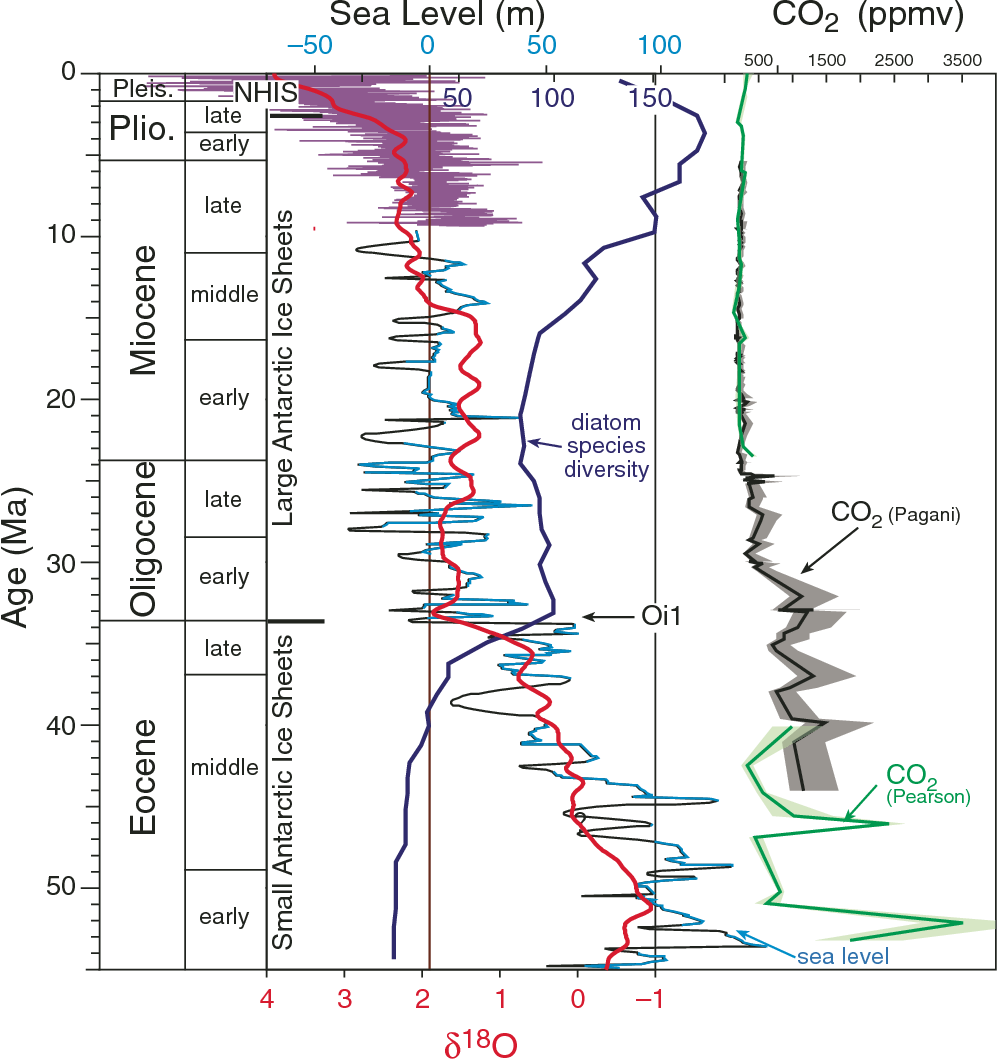
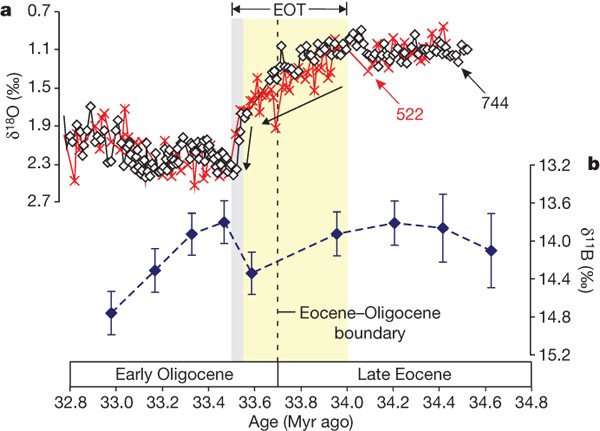
The Eocene-Oligocene E-O boundary 337 million years ago Ma is character-ized by a 15 per mil change in oxygen isotopic d18O values of benthic foraminifera 13 in 300000 years which is indicative of continential ice accumulation and high-latitude cooling and an 1-km deepening of the global calcite compensation depth CCD 2. There is ample evidence for a major global cooling during the EoceneOligocene tran-sition. Although substantial high-latitude sea-surface cooling is largely evident in our records Fig.
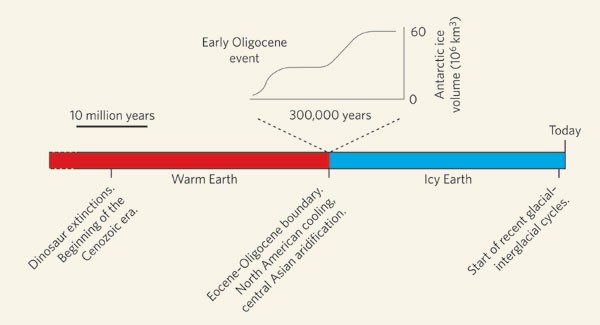
About 34 million years ago Earths climate shifted from a relatively ice-free world to one with glacial conditions on Antarctica characterized by substantial ice sheets. The ice cap survived the period of p CO 2. Indicates an abrupt cooling from 341 to 336 Ma across the EoceneOligocene boundary at 339 Ma.
Previous reconstructions gave no evidence of high-latitude cooling Pagani says. For the first time within Asia a section is mag-. How Earths temperature changed during this climate transition remains poorly understood and evidence for Northern Hemisphere polar ice is controversial.
Tropical sea surface temperature SST and deep ocean records show mixed responses to global cooling across the EoceneOligocene transition EOT with some indicating only modest declines in temperature in the tropics and others showing a 34 C decrease in SST during the first stage of the cooling event EOT-1. Both U K37 and TEX 86 SSTs show substantial high-latitude cooling between 34 and 33 Ma Fig. Turnover in the oceanic plankton included the extinction of the foraminifer Family Hantkeninidae.
High-resolution record of export production in the eastern equatorial Pacific across the Eocene-Oligocene transition and relationships to global climatic records. Our data suggest that a reductioninp CO 2 atm occurredbeforethemainphaseoficegrowth followed by a sharp recovery to pre-transition values and then a moregradualdeclineDuringmaximumice-sheetgrowthp CO 2 atm was between 450 and 1500ppmv with a central estimate of 760ppmv. 2a the determination of mean SST changes during the Eocene-Oligocene climate transition is limited.
34 and 335 Ma is the most profound episode of lasting global change to have occurred since the end of the Cretaceous. The Oligocene climate change was a global increase in ice volume and a 55 m 181 feet decrease in sea level 357335 Ma with a closely related 325255 Ma temperature depression. Paleontological evidence for cooling.
Approximately 34 million years ago across the Eocene-Oligocene transition EOT Earths climate tipped from a largely unglaciated state into one that sustained large ice sheets on Antarctica. During and after the climate transition. Rapid global cooling at the Eocene Oligocene Transition EOT 339335Ma is widely considered to mark the onset of the modern icehouse world.
A large and rapid drop in. Antarctic glaciation is attributed to a threshold response to slow decline in atmospheric CO2 but our understanding of the feedback processes triggered and of climate change on the other contents is. At this transition Van Andel et al 1975.
The stepwise climate change began 325 Ma and lasted through to 255 Ma as depicted in the PaleoTemps chart. Marine proxy data suggest. Cox-all et al 2005 and may have caused changes in carbonate ion activity that masked cooling in MgCa records Lear et al 2004.
Around 34 million years ago at the EoceneOligocene transition the Earth entered a global cooling phase that brought the rapid development of a continental-scale ice cap and associated sea. Mark Pagani professor of geology and geophysics at Yale University says the research found that air and ocean surface temperatures dropped as much as 18 degrees Fahrenheit during the transition. Deep Water Temperature Carbonate Ion and Ice Volume Changes across the Eocene-Oligocene Climate Transition.
The remarkable cooling period in the ocean called the EoceneOligocene transition EOT is correlated with pronounced mamma-lian faunal replacement as shown in terrestrial fossil records.
 Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
 When The World Turned Cold Nature
When The World Turned Cold Nature
 The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
 Pdf Climate Threshold At The Eocene Oligocene Transition Antarctic Ice Sheet Influence On Ocean Circulation Semantic Scholar
Pdf Climate Threshold At The Eocene Oligocene Transition Antarctic Ice Sheet Influence On Ocean Circulation Semantic Scholar
 Antarctic Ice Sheet Variability Across The Eocene Oligocene Boundary Climate Transition Science
Antarctic Ice Sheet Variability Across The Eocene Oligocene Boundary Climate Transition Science
 Fig 4 Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
Fig 4 Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
 The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
 Paleorecords Across The Eocene Oligocene Transition Eot A Benthic Download Scientific Diagram
Paleorecords Across The Eocene Oligocene Transition Eot A Benthic Download Scientific Diagram
 Response Of The Pacific Inter Tropical Convergence Zone To Global Cooling And Initiation Of Antarctic Glaciation Across The Eocene Oligocene Transition Scientific Reports
Response Of The Pacific Inter Tropical Convergence Zone To Global Cooling And Initiation Of Antarctic Glaciation Across The Eocene Oligocene Transition Scientific Reports
 Pdf Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition
Pdf Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition
 Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Through The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Nature
Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Through The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Nature
 Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
Global Cooling During The Eocene Oligocene Climate Transition Science
 Terrestrial Cooling In Northern Europe During The Eocene Oligocene Transition Pnas
Terrestrial Cooling In Northern Europe During The Eocene Oligocene Transition Pnas
 The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
The Enigma Of Oligocene Climate And Global Surface Temperature Evolution Pnas
 Quasi Static Eocene Oligocene Climate In Patagonia Promotes Slow Faunal Evolution And Mid Cenozoic Global Cooling Sciencedirect
Quasi Static Eocene Oligocene Climate In Patagonia Promotes Slow Faunal Evolution And Mid Cenozoic Global Cooling Sciencedirect
 Eocene Oligocene Transition Class Presentation By Kedar Ghimire
Eocene Oligocene Transition Class Presentation By Kedar Ghimire
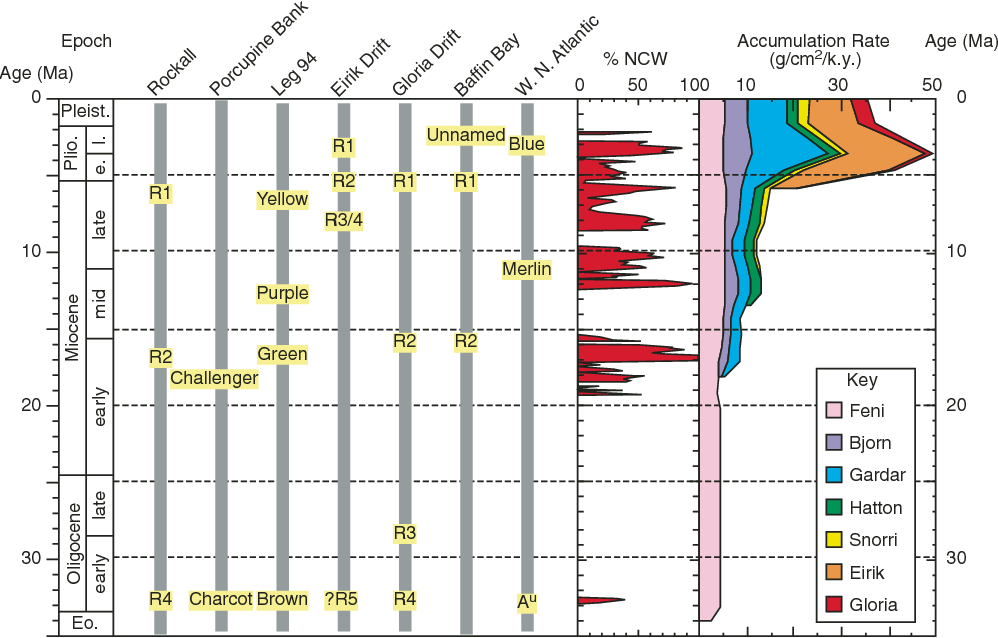 Figure 3 From Climate Threshold At The Eocene Oligocene Transition Antarctic Ice Sheet Influence On Ocean Circulation Semantic Scholar
Figure 3 From Climate Threshold At The Eocene Oligocene Transition Antarctic Ice Sheet Influence On Ocean Circulation Semantic Scholar
 Multiproxy Geochemical Records Of Ocean And Climate Change Across The Download Scientific Diagram
Multiproxy Geochemical Records Of Ocean And Climate Change Across The Download Scientific Diagram
 Oxygen And Strontium Isotopes Co 2 And Insolation During Download Scientific Diagram
Oxygen And Strontium Isotopes Co 2 And Insolation During Download Scientific Diagram
Post a Comment for "Global Cooling During The Eocene-oligocene Climate Transition"